What an administrator is and the functions of a task manager
What is an administrator?
An administrator is the one whose task is to administer . This action can be aimed at a company , an object or a set of objects. The administrator must possess qualities that stand to perform its function properly: have attitude of a leader , having knowledge and experience, know how to act against different adverse situations of moral and intellectual way.
The administrator is in charge of managing the resources of an entity , as well as the designation of positions and tasks to the staff members. As his word says, an administrator will be responsible only and exclusively for administrative work, which is usually strongly related to the financial and economic part of a company.
In buildings or departments it is very common to find the term administrator . Here the individual who has this position will be the one in charge of organizing those tasks related to the maintenance of the building .
Task Manager
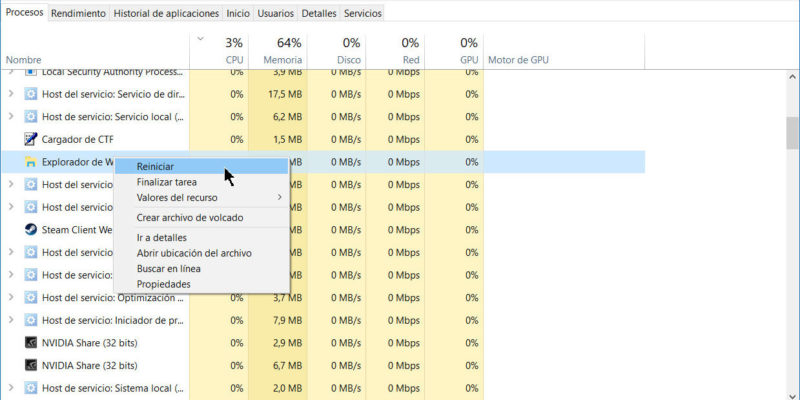
A task manager is a software that has as utility and purpose to provide the user with the information of the different processes and applications that are being executed in the first and second plane by a computer.
Also from the same task manager it is possible to perform the actions of:
- Finish any process .
- Change the priority in which a process is executed (low, below normal, normal, above normal, high, real time).
- Close the user session that you want.
- Start new tasks or applications.
- Observe the performance in terms of CPU usage .
The task manager is a very useful software and the different operating systems have one from the factory . There are also developed by particular manufacturers and can be downloaded from the Internet .
Apostolic Administrator
An apostolic administrator is that bishop or presbyter appointed by the Pope of the Catholic Church to whom he attributes the task of administering a diocese, whose bishop or residential archbishop is not exercising the quota (this situation is called vacant place).
The situation of vacant seat occurs when the residential manager of administering the diocese dies , resigns or an event occurs that produces an inability to administer correctly.
The election of the new administrator, after the occurrence of the vacant seat, is detailed in the Code of Canon Law. It states that after the free quota is left, the new manager must be chosen from among the members of the Diocesan Consultants' College, within a maximum of eight days.
We explain what an operating system is and what it is for. In addition, what types of operating systems exist, and some examples.

What is an Operative System?
It is known as Operating System (OS) to the computer program or group of them that administer a computerized system , both the performance of the physical resources ( hardware ), as the protocols of execution of the digital content ( software ) and the interface with the user . In short, these are programsthat allow and regulate the most basic aspects of the system and without which it could not function properly.
Virtually all computerized devices have some type of operating system, from personal computers , smart phones or specialized calculators.
Operating systems, also called cores or kernels tend to run (ie operate) in a privileged way the rest of the software , without allowing any program make major changes on it that may cause undesired operation. The operating system is the basic operating protocol of the computer, which coordinates all its other functions: communications, processing, user interface, etc.
Many of them consist of graphical interfaces, desktop environments or window managers, which provides the user with a graphic representation of the processes in progress. It can also be a command line, that is, a set of instructions ordered based on their priority and that works based on the user's command and system response.
Most operating systems come pre-installed in new systems , but they can also be replaced or updated by a user who has sufficient administrator privileges .
What is an operating system for?
As has been said, operating systems are an essential part of the operation of computer systems. They are the piece of software central to the chain of processes , since they establish the minimum conditions for the thing to go: the administration of resources, the method of communication with the user and with other systems, the additional applications, etc.
Types of operating system
The Operating Systems can be classified according to the following criteria:
- Task management criteria . They are classified as monotone operating systems, that is, they execute only one program at a time, apart from the OS's own processes; and those multitasking ( multitasking ) that manage the resources of the CPU to achieve a certain simultaneity in the executed processes.
- User administration criteria . We can talk about single-user operating systems, that is, that they allow the control of a single user, and other multi-users, which are managed based on user sessions.
- Criterion of resource management . There are centralized operating systems, limited in their area of influence to a single computer or computer system; and also distributed operating systems, which handle various equipment simultaneously.
Examples of operating system
- Microsoft Windows . Of the most popular that exist, initially it was a set of distributions or graphic operating environments, whose role was to provide other older operating systems such as MS-DOS , a visual representation of support and other software tools. It was first published in 1985 and since then it has been updated to new versions.
- MS-DOS. This is the MicroSoft Disk Operating System (MicroSoft Disk Operating System ), which was one of the most common operating systems for IBM personal computers during the 1980s and mid-90s. It had a series of internal commands and external, displayed on a dark screen sequentially.
- UNIX . This operating system was developed early in 1969, to be portable, multitasking and multi-user. It is really a whole family of similar OSs, some of whose distributions have been offered commercially and others in free format, always from the kernel called Linux.
- MacOS . It is called the operating system of Apple Macintosh computers, and is also known as OSX or Mac OSX. Based on Unix and developed and sold on Apple computers since 2002, it is the most strenuous competition of popular Windows .
- Ubuntu . This operating system is free and open source, that is, everyone could modify it without violating any copyright. It takes its name from a certain ancestral South African philosophy , focused on man's loyalty to his own species above all else. Based on GNU / Linux, Ubuntu is oriented towards ease of use and total freedom , and the British company that distributes it, Canonical, remains providing technical service.
- Android . This operating system based on the Linux kernel, operates on cell phones and tablets and other devices equipped with touch screen. It was developed by Android Inc. and later purchased by Google , thanks to which it is so popular that the sales of Android computer systems surpass those of IOS (for Macintosh cell phones) and those of Windows Phone (for MicroSoft cell phones ).







No comments:
Post a Comment